Feeding and Respiration
Respiration
Due to the cell structure of Sponges, respiration and required gas exchange may be achieved solely through diffusion between the Epithelioid and the ocean (Rupert et al 2009).
Feeding
Sponges are capable of filtering and absorbing particles ranging from 1 – 50 um large. Particles captured by Choanocytes are transported to Archeocytes into the mesohyl where they are digested within the cell (Wheeler 2001). Particles that are too large to be digested are collected by Archeocytes at the inlet canal. Once collected the over sized particles are either expelled at the outlet canal , bypassing the choanocyte chamber, or incorporated into the sponges body (Wheeler 2001).
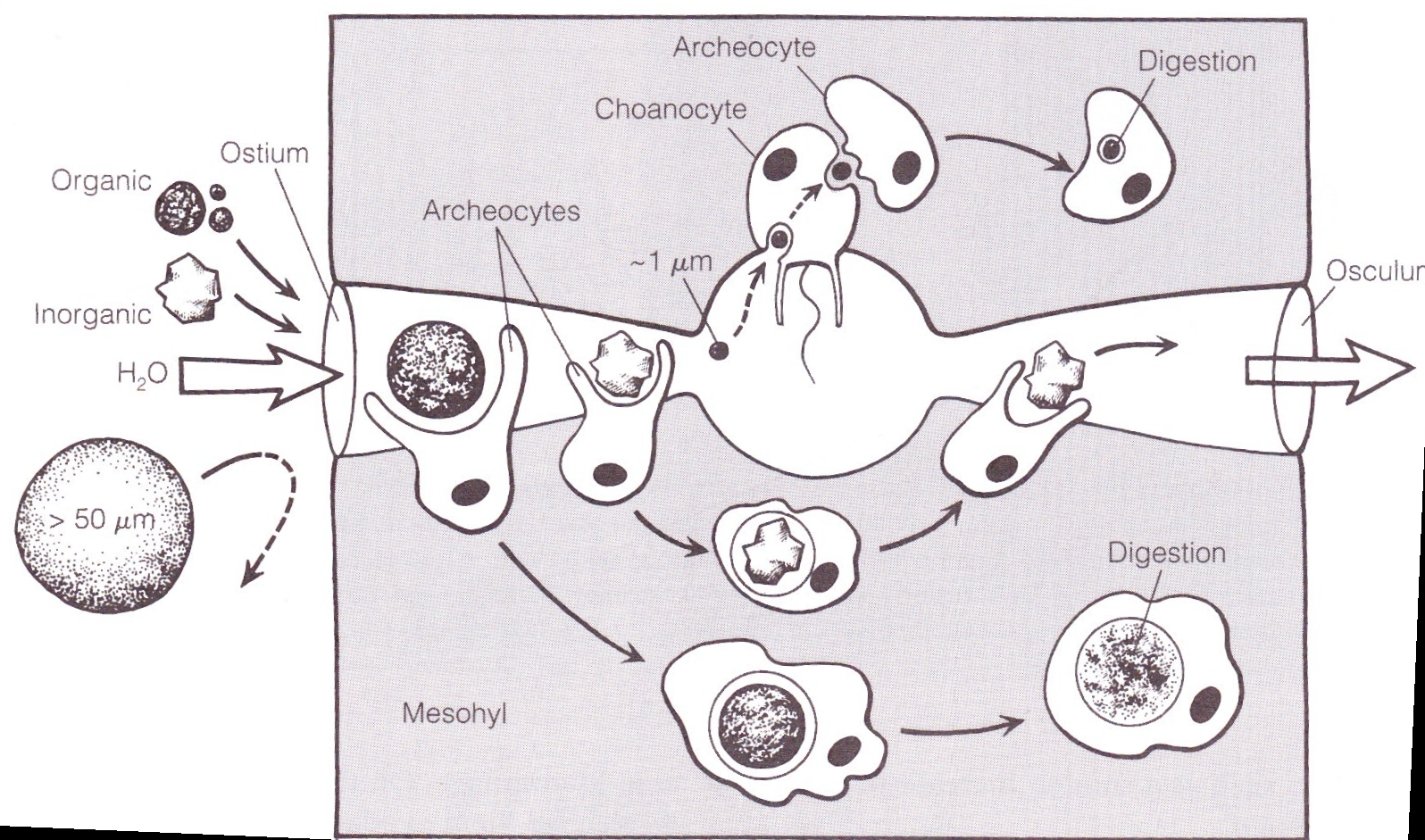
Fig: diagram of feeding system of Porifera. (Rupert et al 2009)
|